
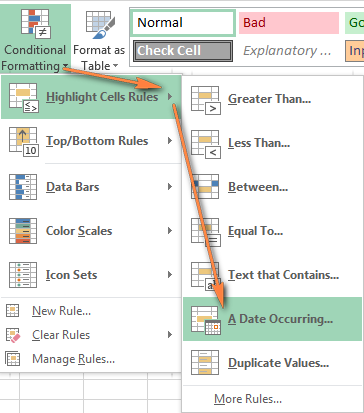
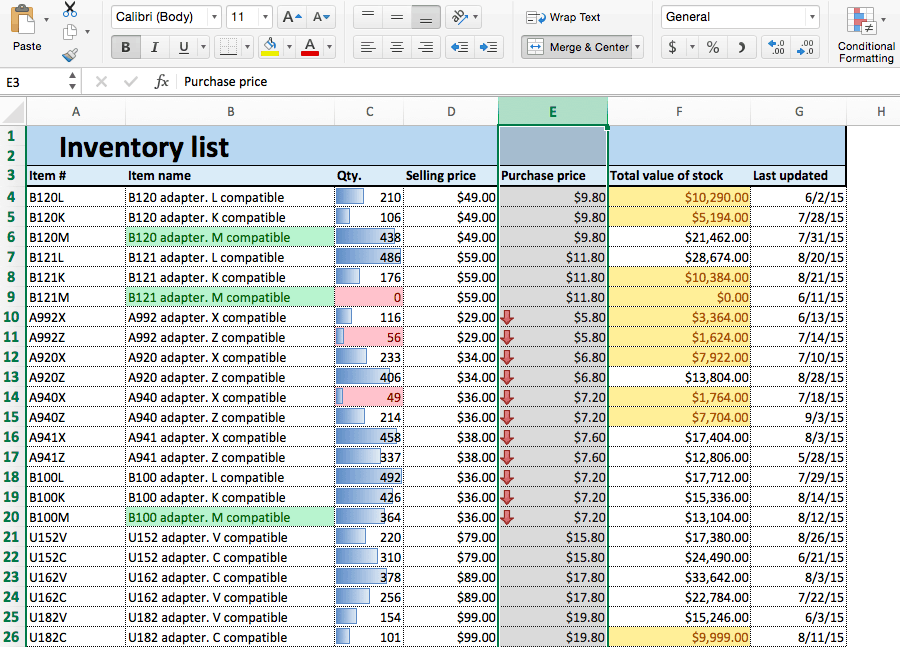
Above average: Values that are higher than the average value are highlighted.Ĭhapter 20: Visualizing Data Using Conditional Formatting Specifying Conditional Formatting.This rule is just one of many numeric value related rules that you can apply. Greater than 10: Values greater than 10 are highlighted with a different background color.You can use a format (such as bright-red cell shading) to make particular cells easy to identify.įigure 20.1 shows a worksheet with nine ranges, each with a different type of conditional formatting rule applied. If not, no formatting is applied.Ĭonditional formatting is a useful way to quickly identify erroneous cell entries or cells of a particular type. If the value is negative, the background is shaded. When you enter or change a value in the range, Excel examines the value and checks the conditional formatting rules for the cell.
For example, you can set things up so that all negative values in a range have a light-yellow background color. About Conditional FormattingĬonditional formatting enables you to apply cell formatting selectively and automatically, based on the contents of the cells. You’ll find a few more conditional formatting improvements in Excel 2010. Microsoft made significant enhancements to conditional formatting in Excel 2007, and it’s now a useful tool for visualizing numeric data. You can apply conditional formatting to a cell so that the cell looks different, depending on its contents.
This chapter explores conditional formatting, one of Excel’s most versatile features.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
